Wi-Fi Password Cracking
Attached is a capture file collected from Wi-Fi network. This capture contains information exchanged during authentication. The capture contains the password in hashed format. Use the hashcat tool to recover the Wi-Fi passwords.
Name: Anurodh Acharya
Attached is a capture file collected from Wi-Fi network. This capture contains information exchanged during authentication. The capture contains the password in hashed format. Use the hashcat tool to recover the Wi-Fi passwords. Prepare a short report explain the WPA 2 authentication dialog. Map the different messages to the packets captured in the pcap file.

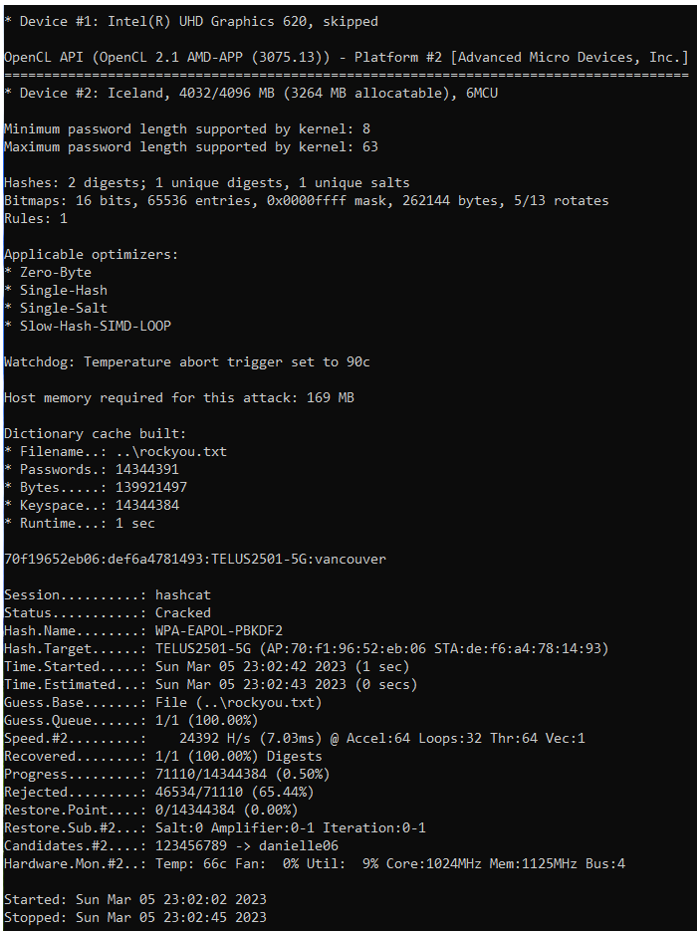

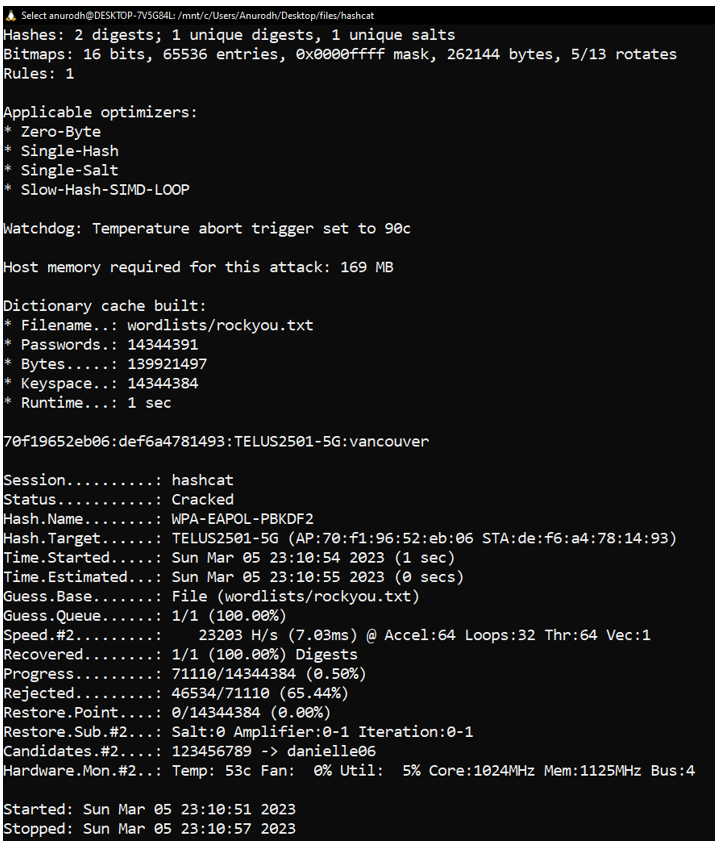

Cracked Password
The cracked password is: vancouver
Wi-Fi SSID
Wi-Fi SSID is: TELUS2501-5G
WPA-2 Authentication
WPA-2 is a security standard for wireless network. It is used for encrypting the data for preventing any unauthorized access. Let us see how does WPA-2 work.
It starts with authentication request. A wireless client wants to connect to WPA2-secured wireless network and it will send authentication request to the router. The router then will respond to this authentication request with a 4-way handshake. The first message from router will be a challenge that will include a random number. The second message this time from the client will be a responds which will include some random number from challenge message which is encrypted with preshared key. Then the third message from router will be another challenge which will include another random number and MIC (Message Integrity Code) for verifying the integrity of the last message. The fourth message from client will be a response message which is going to include new random number that is encrypted with shared key as well as MIC for verifying the integrity of last message. If this 4-way handshake is successful, client and router will have established shared key which can be used for encryption this wireless network traffic. Once this key is established then all of the wireless traffic will be encrypted using an encryption algorithm. For ensuring that encrypted data hasn’t been tampered, WPA2 will also add MIC in each packet.
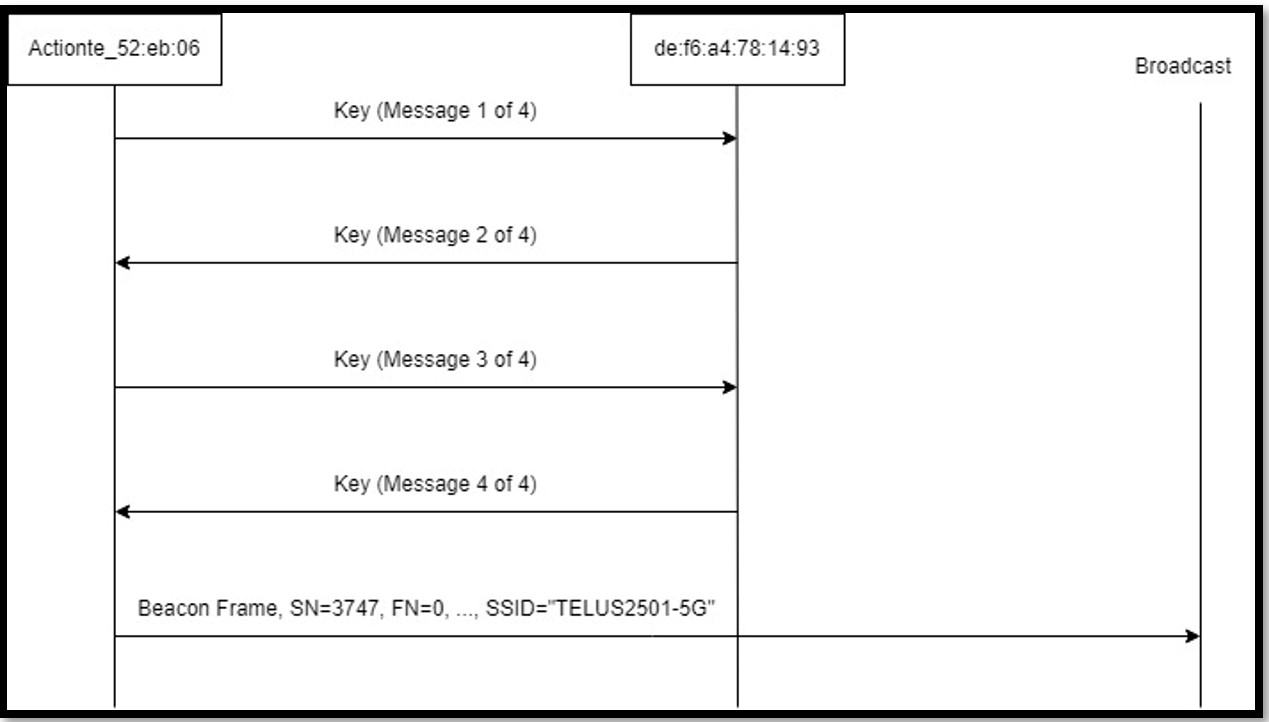
The first packet in the PCAP is a part of 4-way handshake process which is used in WPA2 for secure authentication of the wireless devices.
1. This is the first message in 4-way handshake process where access point and client negotiate a pairwise master key (PMK) for the use in encryption of wireless traffic.
- Source MAC Address: 70:f1:96:52:eb:06
- Destination MAC Address: de:f6:a4:78:14:93
- Protocol: EAPOL
- Length: 175 bytes
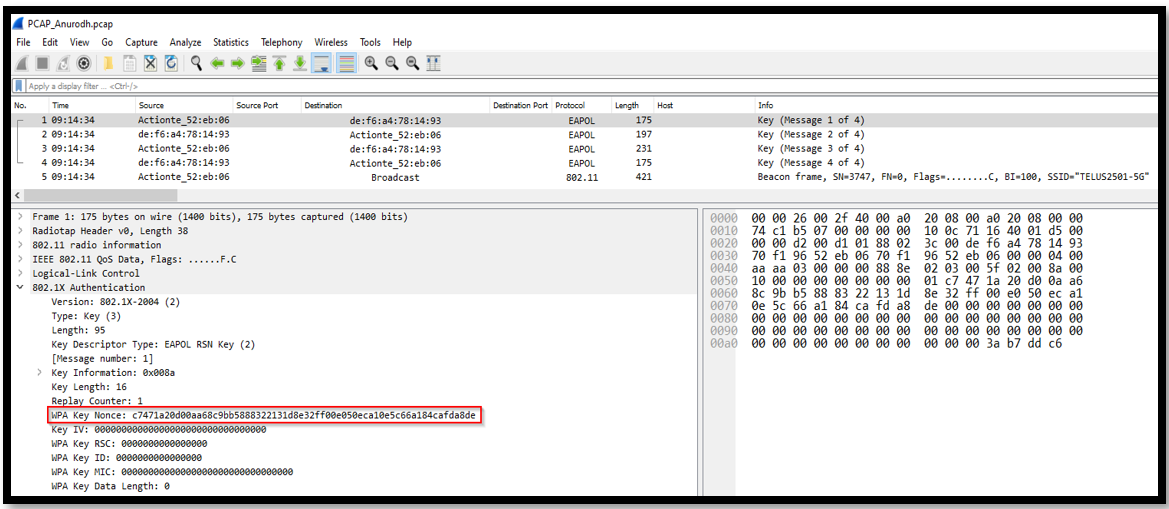
This message is sent from the access point to the wireless client and it includes a nonce which is generated by the access point. Now further in message 2, the client will respond with its own nonce and both of these nonces will be used to derive a shared key called pairwise transient key (PTK) which is used to encrypt all of the wireless data transferred between the client and AP.
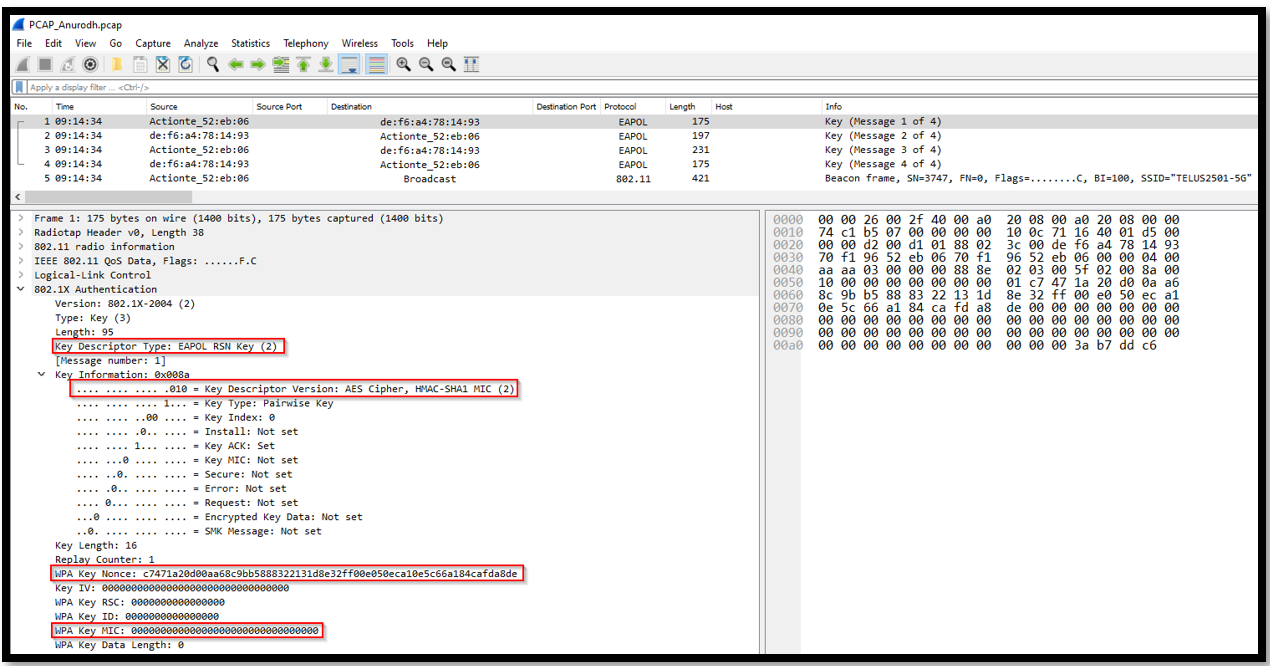
2. This is the second message in 4-way handshake process. This includes wireless client responding to access point with the client’s own nonce. The access point here will be using this nonce as well as the nonce in message 1 for generating the shared key which is called pairwise transient key that is further used to encrypt all of the wireless data between the client and AP.
- Source MAC Address: de:f6:a4:78:14:93
- Destination MAC Address: 70:f1:96:52:eb:06
- Protocol: EAPOL
- Length: 197 bytes :contentReference[oaicite:4]4
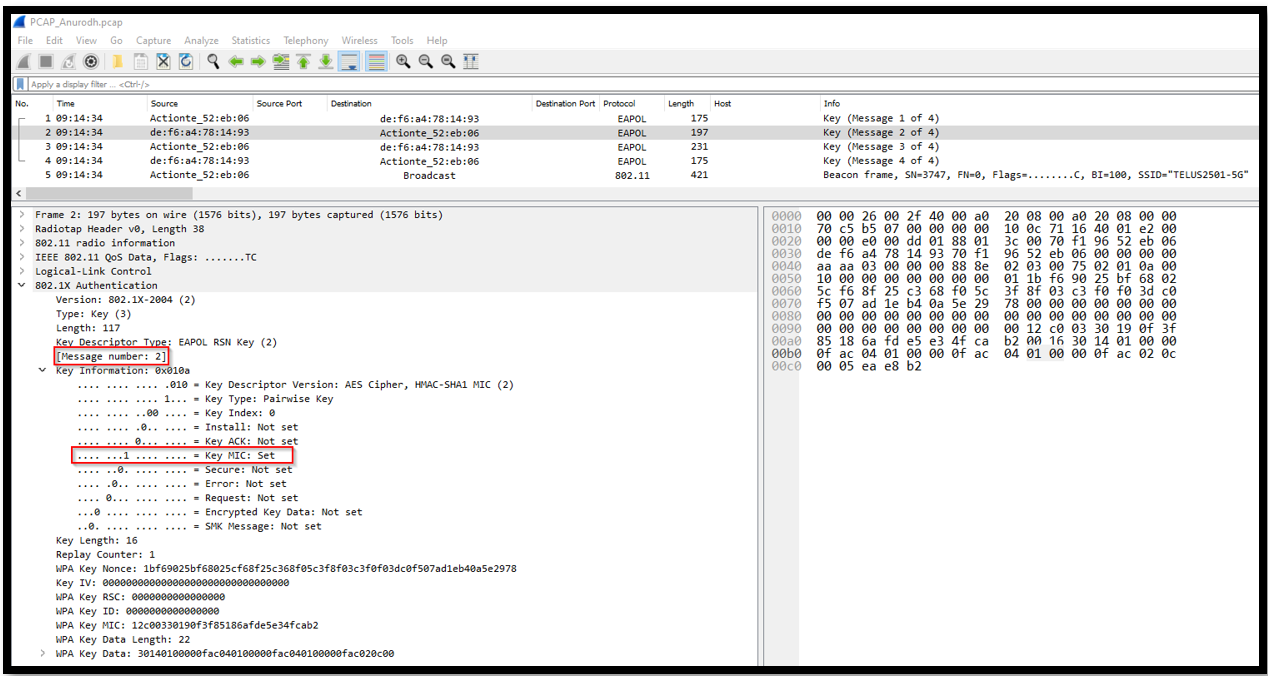
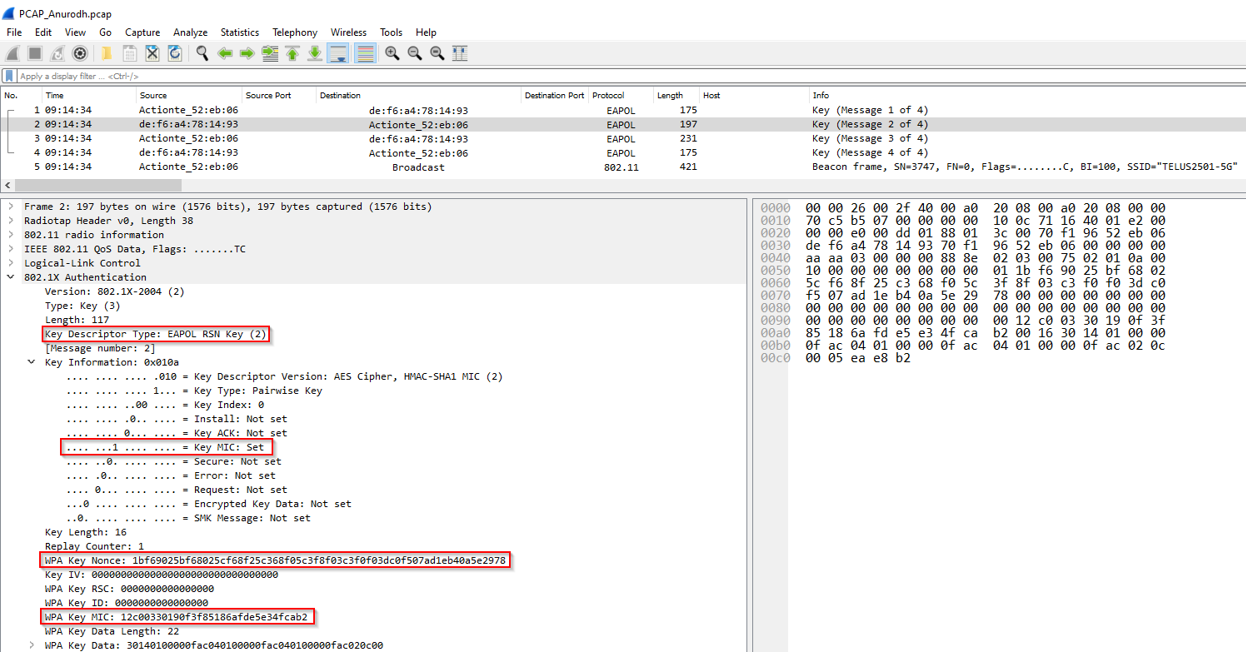
The device sends an EAPOL to the access point with MIC to ensure that AP can verify that the message is corrupted, modified or not. :contentReference[oaicite:5]5
We have the necessary values for generating the PTK. Values which are required to generate the PTK includes Client_Nonce, AP_nonce, source MAC address, Destination MAC address, PMK (we get this from PSK). Further, we will have the KCK that will be derived from PTK for generating the MIC.
3. This is the third message in 4-way handshake process that is used in WPA2. This includes the message integrity code (MIC) that is used for ensuring the authenticity of the previous message. This MIC is calculated using the PTK which was generated from the nonce that were exchanged in the previous process. On receiving this message, client will be verifying the MIC and it will then send the final message of 4-way handshake.
- Source MAC Address: 70:f1:96:52:eb:06
- Destination MAC Address: de:f6:a4:78:14:93
- Protocol: EAPOL
- Length: 231 bytes
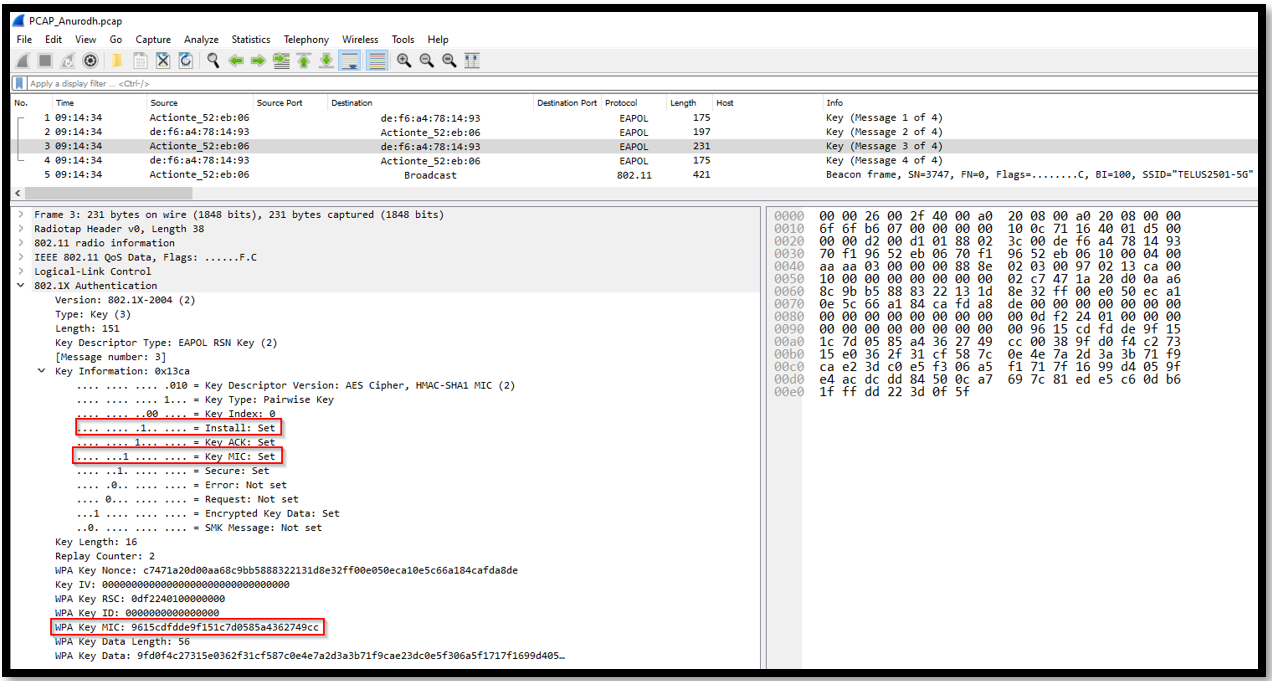
In message 3, the access point will notify the client to install the keys and access point will also send the GTK to the client. We can see the MIC generation in the above message.
Message 4
This is the final message in 4-way handshake process that is used in WPA2. This message includes a MIC that is calculated using the PTK which was generated from nonces exchanged in previous message. Once this message is received, AP will verify the MIC and will consider the wireless client to be authenticated. Now the client and access point will be using the PTK for encryption all of the wireless data between them.
- Source MAC Address: de:f6:a4:78:14:93
- Destination MAC Address: 70:f1:96:52:eb:06
- Protocol: EAPOL
- Length: 175 bytes :contentReference[oaicite:7]7
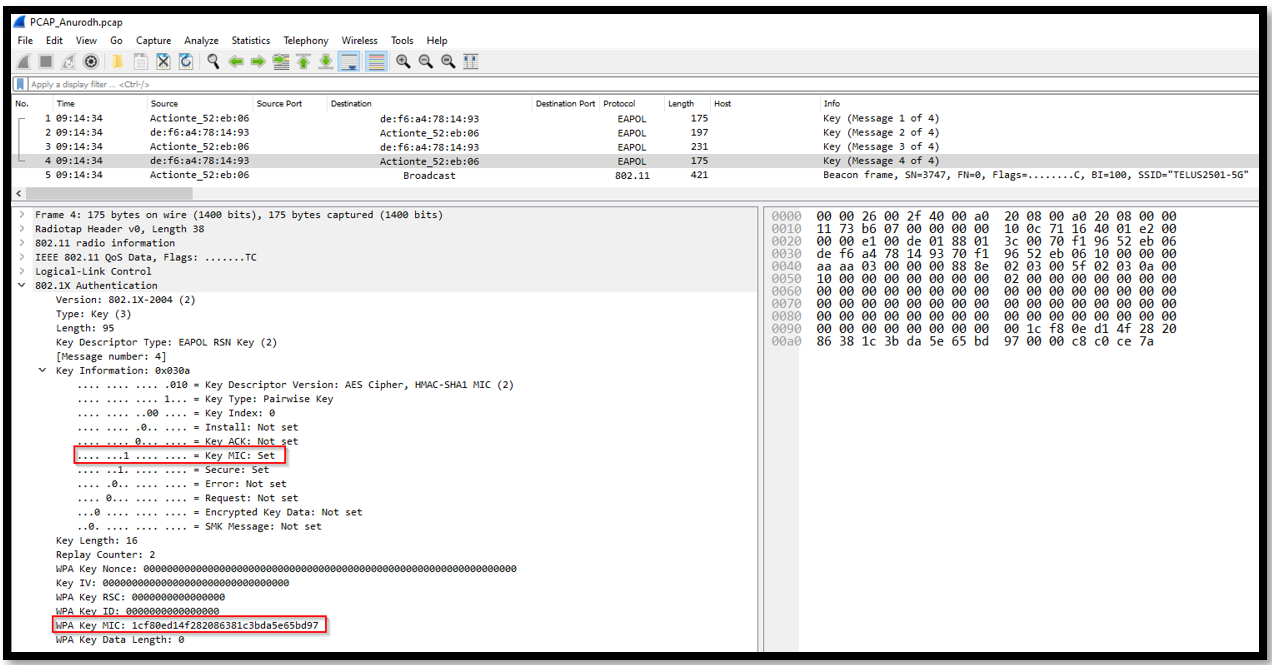
With this message, the 4-way handshake is completed.
5. This is a beacon frame in 802.11 wireless protocol. This is used by access point for broadcasting the information about its network to the nearby clients.
- Source MAC Address: 70:f1:96:52:eb:06
- Destination MAC Address: Broadcast
- Protocol: 802.11
- Length: 421 bytes :contentReference[oaicite:8]8
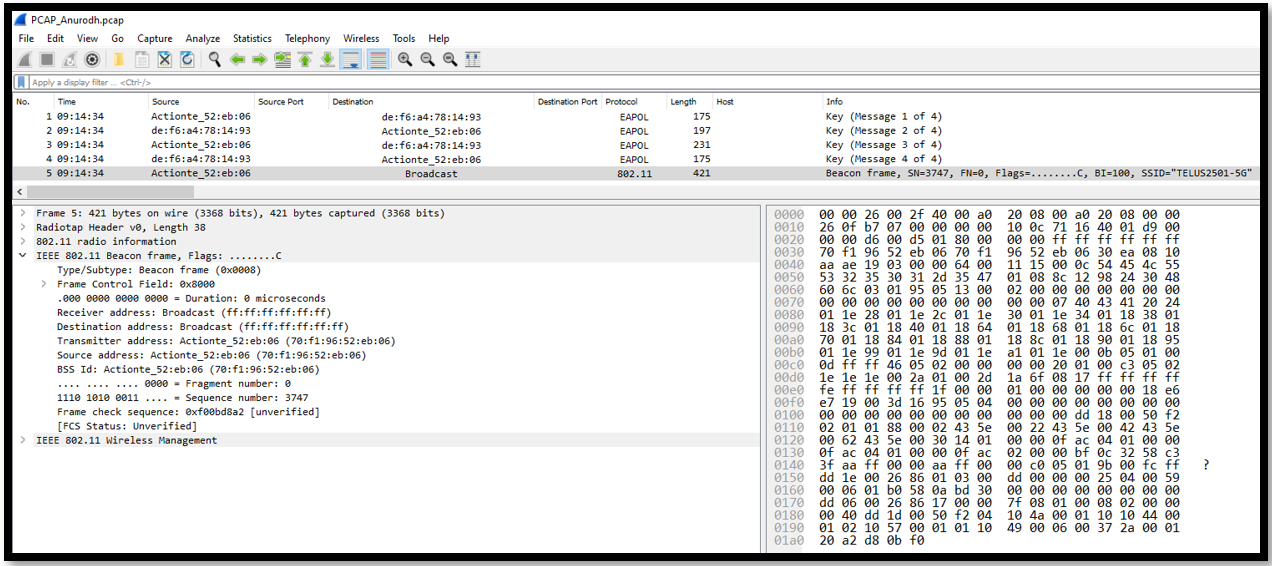
Once the wireless client will receive this packet, it can further use the SSID information for identifying the network and initiating the 4-way handshake with AP for authentication and establishing the secure connection. This can involve exchanging the messages for generating the shared encryption key which can be used for encrypting the transmitted data over wireless network. Overall, this beacon frame enabled the AP to advertise its presence and also give information about the network to any nearby clients.